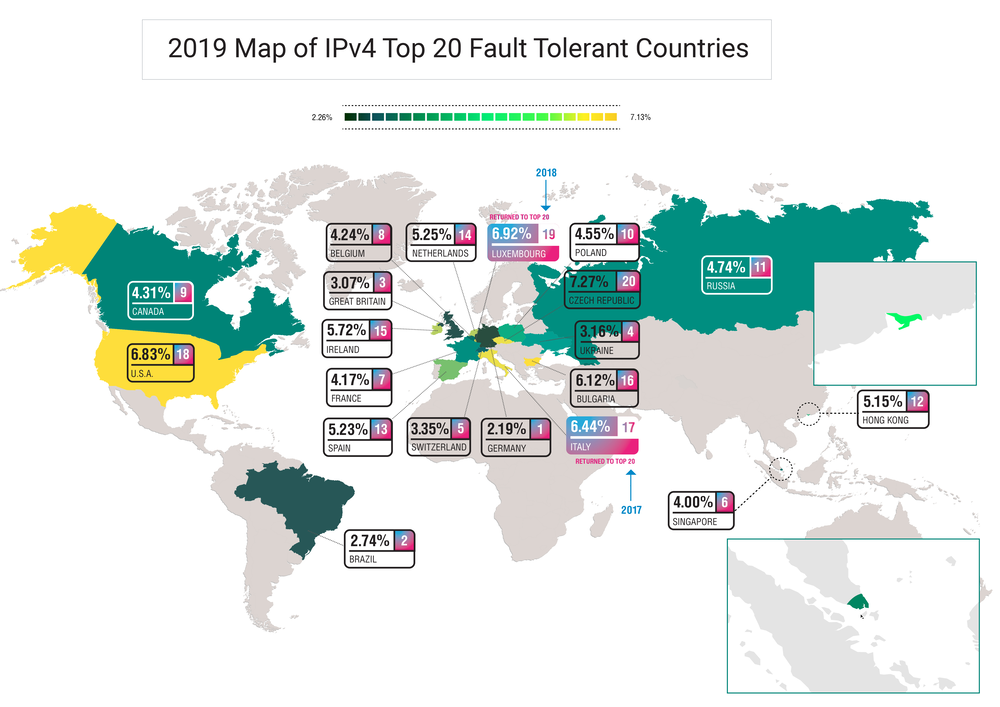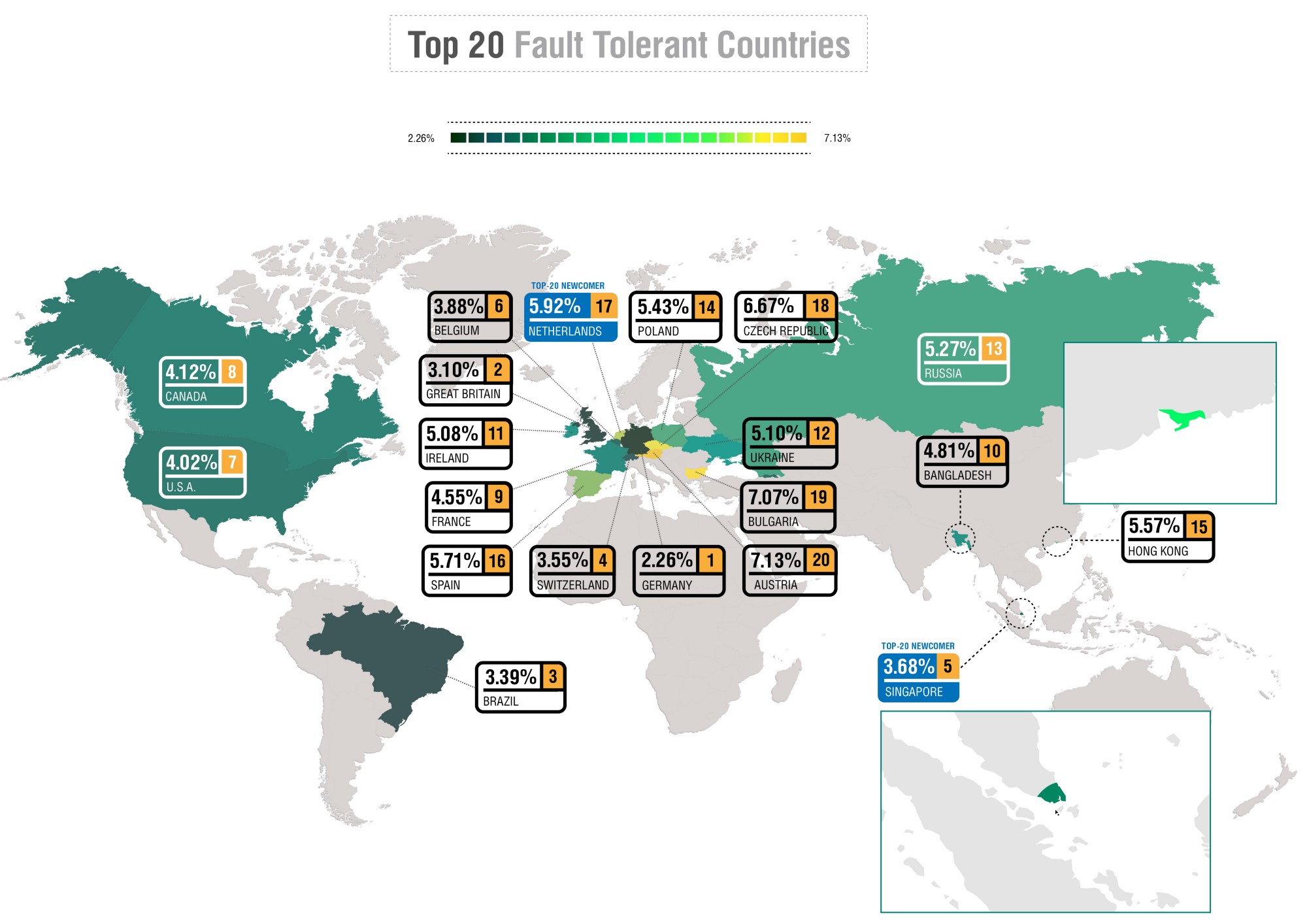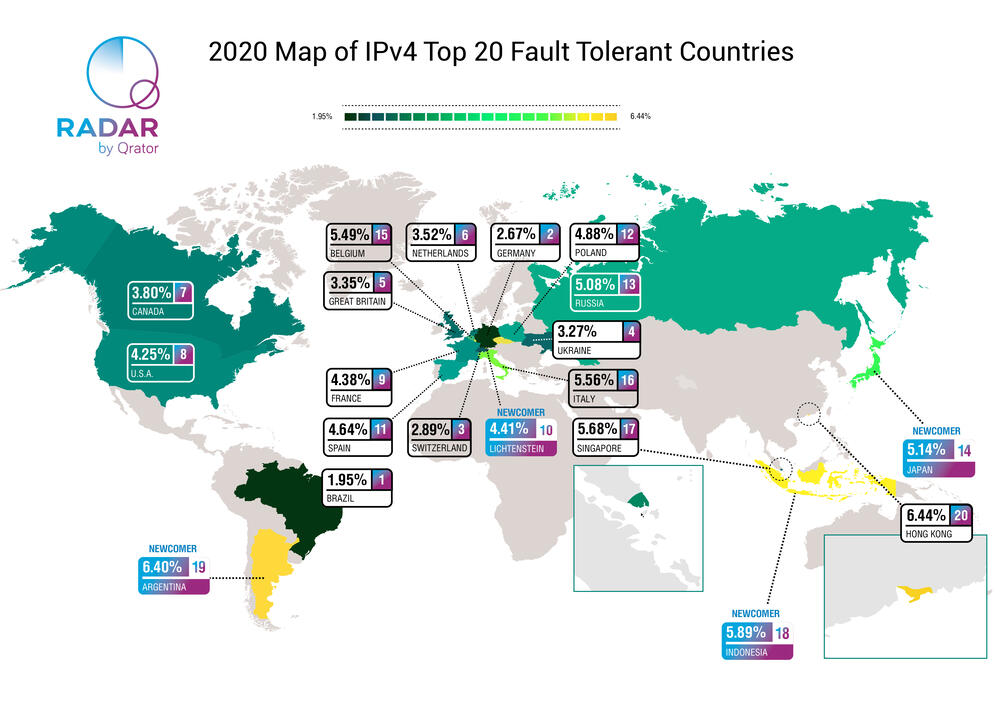
The National Internet Segment Reliability Research explains how the outage of a single Autonomous System might affect the connectivity of the impacted region with the rest of the world. Most of the time, the most critical AS in the region is the dominant ISP on the market, but not always.
As the number of alternate routes between AS’s increases (and do not forget that the Internet stands for “interconnected network” - and each network is an AS), so does the fault-tolerance and stability of the Internet across the globe. Although some paths are from the beginning more important than others, establishing as many alternate routes as possible is the only viable way to ensure an adequately robust network.
The global connectivity of any given AS, regardless of whether it is an international giant or regional player, depends on the quantity and quality of its path to Tier-1 ISPs.
Usually, Tier-1 implies an international company offering global IP transit service over connections with other Tier-1 providers. Nevertheless, there is no guarantee that such connectivity will be maintained all the time. For many ISPs at all “tiers”, losing connection to just one Tier-1 peer would likely render them unreachable from some parts of the world.

 Closely watched events of 2019
Closely watched events of 2019